Springboot - Spring Strarter Security
Spring Security
스프링 시큐리티는 웹 시큐리티, 메소드 시큐리티와 다양한 인증 방법(LDAP, 폼 인증, Basic 인증, Auth)을 지원한다.
3개의 페이지를 만들어 security 를 알아보자.
index, home 페이지는 모든 사용자가 접속하고, my 페이지는 본인만(인가된 사람만) 접근하는 것을 만들것이다.
스타터 웹과 타임리프를 의존성에 추가한다.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>컨트롤러를 등록하자.
@Controller
public class HomeController {
@GetMapping("/home")
public String home() {
return "home";
}
@GetMapping("/my")
public String my() {
return "my";
}
}
컨트롤러를 등록하는 방법은 Controller를 클래스위에 등록하는 방법 외에도 ViewController 를 쓰는 방법도 있다.
@Configuration public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/home").setViewName("home"); } }
resources/template/ 에 리소스를 만든다.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Index</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome</h1>
<div>
<span>Go to</span>
<a href="/home">HOME</a>
<span> or </span>
<a href="/my">MY</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>home.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Home</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Home</h1>
</body>
</html>my.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>My</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My</h1>
</body>
</html>이렇게 해놓고, 스프링어플레키션을 실행시키고 브라우저로 url을 요청하면 화면이 잘 나올 것이다.
컨트롤러 테스트코드도 만들어보자.
@WebMvcTest(HomeController.class)
class HomeControllerTest {
@Autowired
MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
public void home() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/home"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(view().name("home"));
}
@Test
public void my() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/my"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(view().name("my"));
}
}잘 작동한다.
Spring Security
이제 시큐리티를 알아보자.
스프링 시큐리티 의존성을 추가한다.
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>테스트 코드를 다시 실행해보자. 에러가 난다.
MockHttpServletResponse:
Status = 401
Error message = Unauthorized
Headers = [WWW-Authenticate:"Basic realm="Realm"", X-Content-Type-Options:"nosniff", X-XSS-Protection:"1; mode=block", Cache-Control:"no-cache, no-store, max-age=0, must-revalidate", Pragma:"no-cache", Expires:"0", X-Frame-Options:"DENY"]
Content type = null
Body =
Forwarded URL = null
Redirected URL = null
Cookies = []에러메시지 unauthorized 와 함께 401 에러가 발생한다. 스프링 시큐리티를 추가한 순간 모든 요청에 대해 인증이 필요하게 된 것이다.
스프링시큐리티가 제공하는 스프링시큐리티 자동설정이 적용되었기 때문이다.
여기에 basic 인증과 폼 인증이 둘 다 적용된다.
여기서 헤더에 보면 Authenticate:"Basic realm="Realm" 이라는 문구가 있는데, Basic 인증 요청을 요구하고 있다.
이는 헤더의 accept 헤더에 따라 종류가 달라질 수 있다.
브라우저는 응답을 받을 때 기본적으로 accept header 를 HTML 로 원한다. 이럴 경우 폼 인증으로 넘어간다.
따라서 요청시 accept 헤더를 변경해서 html 형태로 주면 브라우저는 응답을 받을 수 있게 된다.
public void home() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/home")
.accept(MediaType.TEXT_HTML))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(view().name("home"));
}MockHttpServletResponse:
Status = 302
Error message = null
Headers = [X-Content-Type-Options:"nosniff", X-XSS-Protection:"1; mode=block", Cache-Control:"no-cache, no-store, max-age=0, must-revalidate", Pragma:"no-cache", Expires:"0", X-Frame-Options:"DENY", Location:"http://localhost/login"]
Content type = null
Body =
Forwarded URL = null
Redirected URL = http://localhost/login
Cookies = []여전히 에러가 나오긴 하지만 응답 코드가 302로 바뀐것을 알 수 있다.
http://localhost/login 로 리다이렉트 하라는 응답이 돌아온 것이다. (폼 인증을 해야된다.)
서버 실행
이제 테스트코드 말고, 애플리케이션을 실행시켜보자.
애플리케이션을 실행시키면 로그인 페이지가 제공된다.
기본 username은 "user" 이며, password 는 애플리케이션 실행시 마다 run 창에 출력해준다.
Using generated security password: 32c0cd01-****-****-****-f5049c832963application.properites 에서 username과 password 를 정할 수도 있다.
spring.security.user.name=
spring.security.user.password=
테스트
시큐리티 테스트 의존성을 추가한다.
pom.xml
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.security/spring-security-test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>@WebMvcTest(HomeController.class)
class HomeControllerTest {
@Autowired
MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
@WithMockUser
public void home() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/home")
.accept(MediaType.TEXT_HTML))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(view().name("home"));
}
@Test
@WithMockUser
public void my() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/my"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(view().name("my"));
}
}@WithMockUser 어노테이션을 붙이면, 가짜 username 과 password 를 요청에 제공해주어서, 인증 페이지를 통과할 수 있게 된다.
즉, 테스트가 성공하게 되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
스프링부트 시큐리티의 자동설정
시큐리티의 설정파일 중 하나는 SecurityAutoConfiguration 이다.
이벤트 퍼블리셔가 등록되어 있어서 아래 이벤트 발생시 핸들러를 등록해서 조치를 취할 수 있다.
BadCredentialsExceptionUsernameNotFoundExceptionAccountExpiredException등등 많음
스프링부트에서 제공하는 시큐리티 설정파일은 SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration 이다. 안에 구현된 코드를 보면 기존 스프링 시큐리티에서 제공하는 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 의 기본 설정을 그대로 따르고 있는 것을 볼 수 있다. 이 중 HttpSecurity 가 주요한 설정이다.
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
this.logger.debug("Using default configure(HttpSecurity). If subclassed this will potentially override subclass configure(HttpSecurity).");
((HttpSecurity)((HttpSecurity)((AuthorizedUrl)
// 모든 요청을 가로채서 인증을 하게 하고
http
.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest()).authenticated()
// 폼로그인을 사용하고
.and()).formLogin()
// httpBasic을 사용한다.
.and()).httpBasic();
}
또 다른 설정파일로는 UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration 가 있다. 스프링 애플리케이션이 구동 될 때 인메모리 서비스를 만들어 username, password를 생성하여 제공한다. 이 설정을 쓰고 싶지 않다면 ConditionalOnMissingBean 어노테이션에 들어있는 UserDetailsService 등을 빈으로 사용하여 수정하면 된다.
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(
value = {AuthenticationManager.class, AuthenticationProvider.class, UserDetailsService.class}...}
public class UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration {
...대부분의 프로젝트가 UserDetailsService 를 직접 구현하여 사용할 것이다.
예제
1. Web Security 설정
위의 예제를 이어서 보자.
우리가 원하는 것은 "/", "/home" 은 모두가 접속할 수 있고, "/my" 는 인증된 사람만 접속하는 것이다. 그런데 기본 설정은 모두 인증을 받아야 들어갈 수 있다. 이를 수정하려면 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 를 상속받아 커스터마이징하면 된다.
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 를 상속받아 커스터마이징 하는 순간 SpringBootWebSecurityConfiguration 의 설정은 무시되게 된다.
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.httpBasic();
}
}이렇게 하면 "/", "/home" 은 모든 사용자의 접근 인가가 허용되고, 나머지는 인증을 해야 들어갈 수 있다. 물론 "/my" 만 인증이 필요한 것이면 다른 조작이 필요할 것이다.
2. UserDetailService
위처럼 하면, 스프링부트가 구동될 때마다 스프링부트가 만들어준 콘솔에 찍힌 password 로 접속해야 한다. 실제 이런일은 없을 것이다. 사용자들은 각자의 아이디가 있고 비밀번호가 있다.
username과 password를 데이터베이스에 저장하고, 이를 사용해서 인증을 하도록 구성해보자. 여기서는 jpa와 h2 database 를 사용할 것이다.
Account 패키지를 만든다.
@Getter @Setter
@Entity
public class Account {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
private String username;
private String password;
}public interface AccountRepository extends JpaRepository<Account, Long> {
Optional<Account> findByUsername(String username);
}이렇게 데이터베이스 설정과 연동은 완료되었다. 우리는 로컬에서 런타임에 아이디, 비밀번호를 만들어서 인메모리 db인 h2 에 인증정보를 저장할 것이다.
이제 로그인 정보를 생성하는 서비스를 만들어보자.
@Service
public class AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountRepository accountRepository;
public Account createAccount(String username, String password) {
Account account = new Account();
account.setUsername(username);
account.setPassword(password);
return accountRepository.save(account);
}
}그리고 스프링부트 시큐리티의 자동설정 기능인 UserDetailsServiceAutoConfiguration 에서 사용하는 UserDetailsService 를 커스터마이징한다. 이는 username 을 입력받아서 DB 에서 찾을 수 없으면 에러를 내보내고, 있으면 스프링 시큐리티가 제공하는 User() 객체에 인가를 담아 보낸다.
@Service
public class AccountService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private AccountRepository accountRepository;
...
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
Optional<Account> byUsername = accountRepository.findByUsername(username);
Account account = byUsername.orElseThrow(() -> new UsernameNotFoundException(username));
return new User(account.getUsername(), account.getPassword(), authorities());
}
private Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities() {
return Arrays.asList(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_USER"));
}
}
이제 애플리케이션 러너로 런타임시 아이디와 비밀번호를 만들어서 DB에 저장하도록 해보자.
@Component
public class AccountRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
AccountService accountService;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
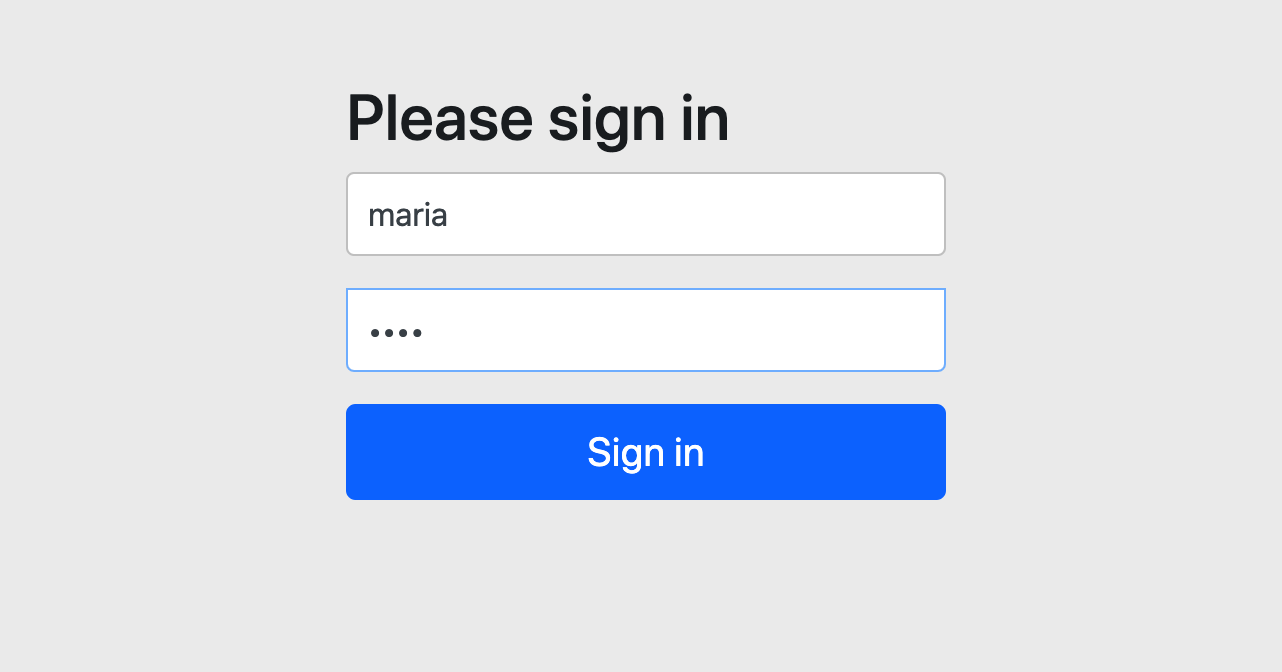
Account maria = accountService.createAccount("maria", "1234");
System.out.println(maria.getUsername() + " pw: " + maria.getPassword());
}
}이제 애플리케이션을 구동해보면, 실행이 잘된다. "/" 와 "/home", "/my" 모두 잘들어가지고, "/my" 에서만 폼 인증 화면이 나온다.
하지만 아이디와 비밀번호 입력시 화면은 바뀌지 않고, 콘솔에 아래와 같은 에러가 발생한다.
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: There is no PasswordEncoder mapped for the id "null"이는 비밀번호 인코딩을 하지 않았기 때문이다.
3. PasswordEncoding
패스워드를 아무 인코딩도 하지 않고 DB 에 저장하게 되면 매우 큰 보안 이슈를 일으키게 된다. 따라서 인코딩을 해주어야한다. 다양한 패스워드 인코딩을 하는 방식이 있다.
인코딩을 회피하는 방법으로는 아래 방법이 있다.
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
...
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
}웹 보안 설정파일에 NoOpPasswordEncoder 를 설정하여 패스워드 인코딩을 회피하는 방법이 있다. 이렇게 되면 패스워드 앞에 (noop) 접두어가 붙으면서 인증 시스템이 이것을 읽고 인증을 허가하게 된다. 하지만 실제 서비스 운영에서는 절대 쓰면 안되는 방법이다...
그 대신 아래 방법을 사용한다.
@Configuration
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
...
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
// 인코더를 반환한다.
return PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder();
}
}
이제 서비스에서 로그인 정보를 만들 때 인코딩된 비밀번호를 만들도록 하면 된다.
@Service
public class AccountService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private AccountRepository accountRepository;
// password 인코더를 추가해준다.
@Autowired
private PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
public Account createAccount(String username, String password) {
Account account = new Account();
account.setUsername(username);
account.setPassword(passwordEncoder.encode(password)); // 패스워드 인코딩 후 set 한다.
return accountRepository.save(account);
}
...
}그리고 다시 애플리케이션을 구동시키고 maria, 1234를 입력해보자.
성공적으로 접속이 된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
'Java, Kotlin, Spring > Spring, Spring Boot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Springboot - Actuator, 운영 (0) | 2021.01.21 |
|---|---|
| Springboot - Spring REST Client (0) | 2021.01.21 |
| Spring Data - MongoDB (0) | 2021.01.21 |
| Spring Data - Redis (0) | 2021.01.21 |
| Spring Data - Neo4j 사용 (0) | 2021.01.20 |





댓글